919 -- Unification : algorithmes et applications.
De AgregmathKL
Révision de 1 juin 2012 à 21:38 par Basile (discuter | contributions) (→Plan Basile et Kévin (2012))
"Rien"
Le jury (s'il était unifié à {LMB}).
Sommaire
Plan Basile et Kévin (2012)
Le plan
Intro : motivation de l'intérêt de l'unification pour le typage. Exemple avec Ocaml.
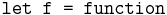
![\;{\texttt {|\ []\ ->\ (fun\ y\ ->\ [y])}}](/images/math/f/c/c/fcc2ac43c7f524ed59eca4a682101310.png)
I - Unification
- Langage du premier ordre et termes.
- Substitutions
- Definition, exemples
- Autre chose
- Unification
- Definition exemple
- Unificateur principal
II - Algorithmes
- Naïf
- Celui de Stern
- Celui de AllThat (si différent)
- Evolué
- Union-find et termes en DAG (AllThat)
III - Applications
- Réécriture
- Definitions
- Confluence locale
- Developpement : Lemme des paires critiques (AllThat)
- Logique
- Méthode de résolution
- Developpement : Complétude de la méthode de résolution (Stern)
- Le langage Prolog
- Méthode de résolution
- Typage
Développements Possibles
Proposés
Possibles
Références
- Baader, Nipkow : Term Rewriting and All That
- J. Stern : Fondements mathématiques de l'informatique
- Weis, Leroy : Le langage Caml